About audio and video sources
This feature is available in NVivo Pro and Plus editions. Learn more
You can import your audio or video files and analyze the content in NVivo—this topic provides an introduction to working with audio and video sources and provides links to other useful topics.
In this topic
- Understand audio and video sources
- Open and navigate audio and video sources
- What can I do in an audio or video source?
- Organizing audio and video sources
- Can I work with the transcript only?
- Are imported media files always stored inside my project?
- Where are YouTube videos stored?
- Can I embed a YouTube video in my project?
Understand audio and video sources
You can create an audio or video source by importing media in a supported format. If you want to work with YouTube videos, you can create a video source that is linked to the video on YouTube—refer to Import from YouTube for more information.
NOTE If you are working with YouTube videos in a shared project, make sure that all team members are using the same version of NVivo.
A video or audio source consists of a media file and a transcript:
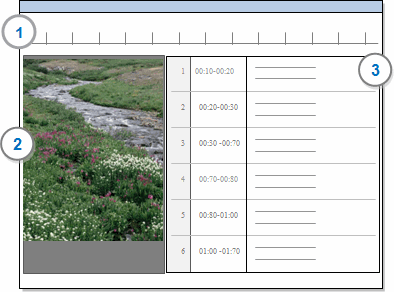
1 Media timeline—you can play, code and annotate the media using the timeline.
2 Media—you can resize the display and use the controls to play, pause and rewind
3 Transcript—you can import a transcript or play and transcribe the media in NVivo.
You can also have your media professionally transcribed using an integrated transcription service provided by TranscribeMe.
Open and navigate audio and video sources
You can double-click an audio or video source in List View to open it in Detail View.
When you are working with the transcript, you can
-
Use the vertical and horizontal scroll bars to move up, down, left or right in the transcript.
-
Find specific words or phrases—refer to Find and replace text.
-
You can use ' Go To' to jump to a point on the timeline, a transcript row, see also link or annotation.
When you are working with the media, you can use the Playback group commands on the Media tab to play, pause, stop and move forwards and backwards in the media file. You can also click and drag the seek slider, to position it on the timeline.
If you use zoom to magnify the timeline, you can use the horizontal scrollbar below the timeline to move the timeline to the left or right. Refer to Customize the audio or video display for more information.
What can I do in an audio or video source?
When working in an audio or video source you can:
-
Create a transcript—you can transcribe the media in NVivo, you can import an existing transcript or you can send your media source for transcription via an integrated transcription service provided by TranscribeMe. If you don't need a transcript, you can leave it blank (and hide it if you want to).
-
Play, pause, forward and rewind the media—you can go to an exact location using the timeline
-
Code the media directly on the timeline or code the text in the Content column of the transcript
-
Annotate the media directly on the timeline or annotate text in the Content column of the transcript.
-
Create see also links from the timeline or text in the Content column of the transcript
Organizing audio and video sources
You store audio and video sources under the Internals system folder in Navigation View. You can create sub folders under the Internals folder to organize your audio and video sources.
If you captured the comments from a YouTube video, then on import, a folder is created that includes the video source and a dataset source containing the comments.
Can I work with the transcript only?
You can work with a transcript, even if the audio or video is not available. For example, if
-
You are working in the field and the media is stored on a network drive at the office.
-
You are working with a video source containing YouTube content, but are not connected to the Internet.
When you open an existing audio or video source where the content is not available, you are prompted to work without the audio or video. If you choose this option, the source opens and you can work with the transcript.
You can also create an audio or video source without the media content. This is useful in situations where you have a transcript, but do not have the original recording.
Are imported media files always stored inside my project?
The media content in an imported audio/video source can be embedded in the project or stored outside of the project on your computer or network. Storing media outside of the project is useful when you are dealing with many or very large media files—embedding large files can impact on project performance. Refer to Store audio and video files to understand your options for storing media files.
The way you work with audio and video (coding, linking and annotating) is the same whether the media file is embedded or stored outside the project.
Where are YouTube videos stored?
A YouTube video is not embedded in the project or stored on your computer or network. The video source has a link to the video on YouTube.
You need an Internet connection and Internet Explorer 10 (or later) to play the video in NVivo. You can still work with the video transcript (if you have created one) without an internet connection.
You can work with a video source from YouTube in the same way as you would a video source containing imported media—however, there are few minor differences. For videos sources from YouTube:
-
You cannot display a waveform.
-
You cannot adjust the playback speed.
-
The video size always scales to fit the player window.
Refer to Import from YouTube for more information.
Can I embed a YouTube video in my project?
No, you cannot embed a YouTube video in NVivo. You create a video source that links to the original content on the YouTube website. This is a restriction that is imposed by YouTube.
Refer to Import from YouTube for more information.


 Top of Page
Top of Page